Bienvenido Santos
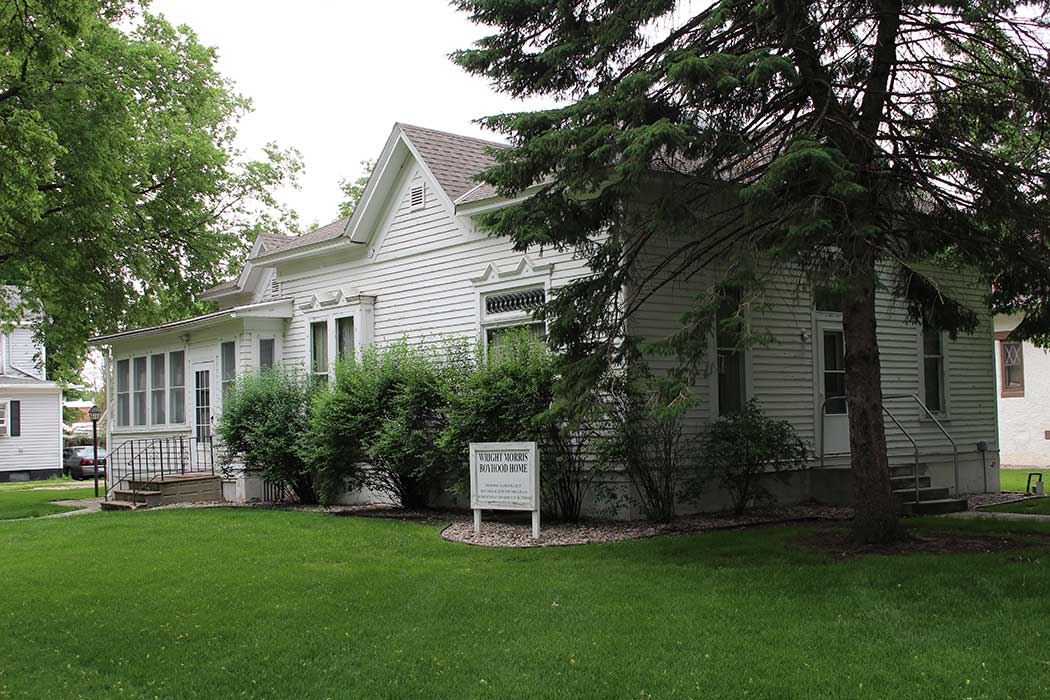
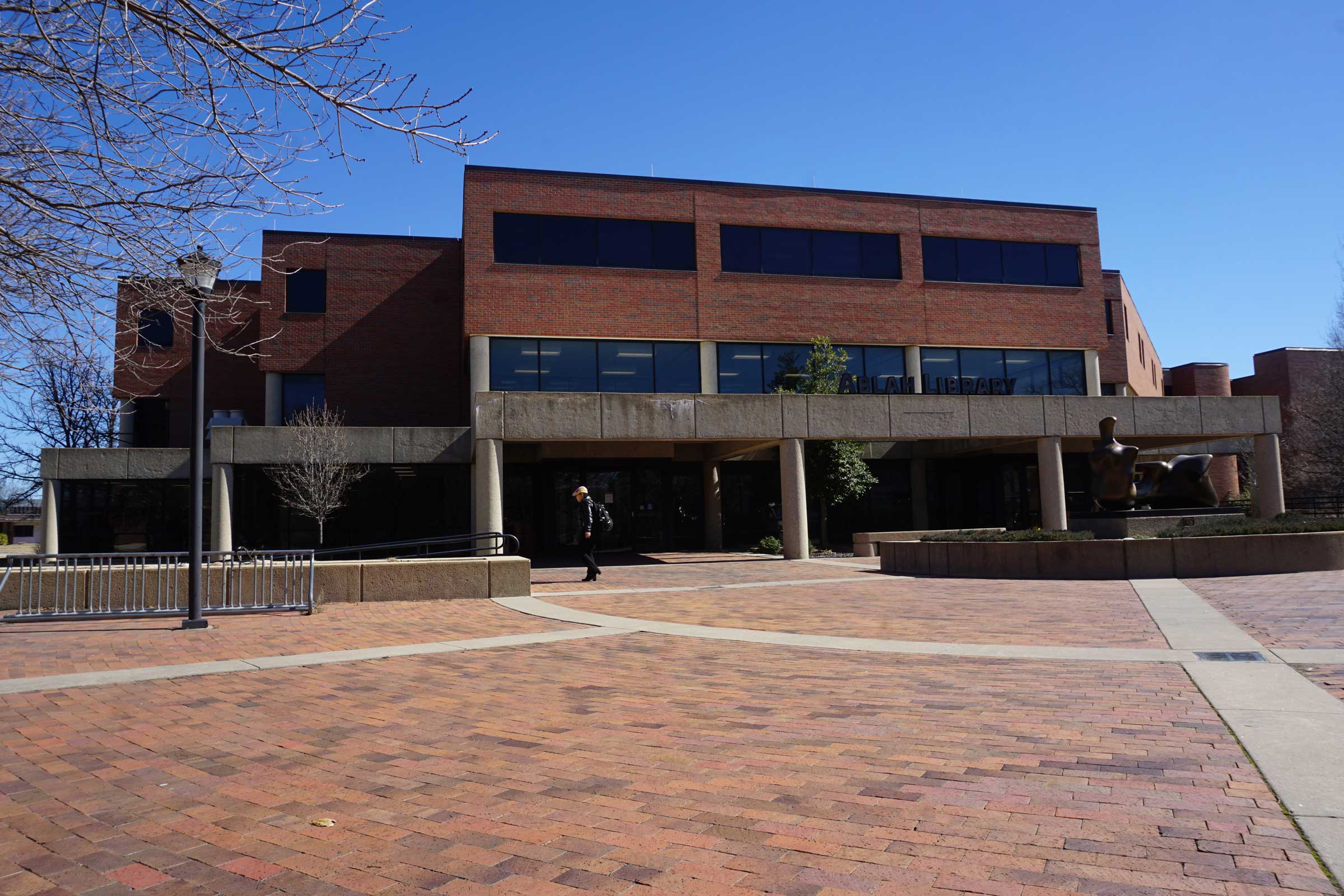
Ablah Library
Wichita, Kansas
By Abby Bayani-Heitzman
Filipino American writer Bienvenido “Ben” N. Santos had a complicated relationship with the Midwest. He first arrived in the United States in 1941 as a pensionado, or government-sponsored scholar, to study at the University of Illinois. After World War II, he settled into a career as an educator and taught as a Fulbright exchange professor at the University of Iowa before arriving in 1973 at Wichita State University. He served as a Professor of Creative Writing and Distinguished Writer in Residence until 1982, a period that coincided with his voluntary exile from the Philippines.
During the dictatorship of Philippine President Ferdinand E. Marcos (1965–1986), Santos’ 1982 novel The Praying Man was banned for its perceived criticism of the Marcos regime due to its depiction of political corruption. Although living and working in the Midwest kept Santos free from political persecution, it also distanced him from the country and culture he loved.
I first learned about Ben Santos and his writing while I was a student at Wichita State; as a Filipino American and aspiring writer in Kansas, his story really resonated with me, not least because of his ties to both the Philippines and the Midwest.
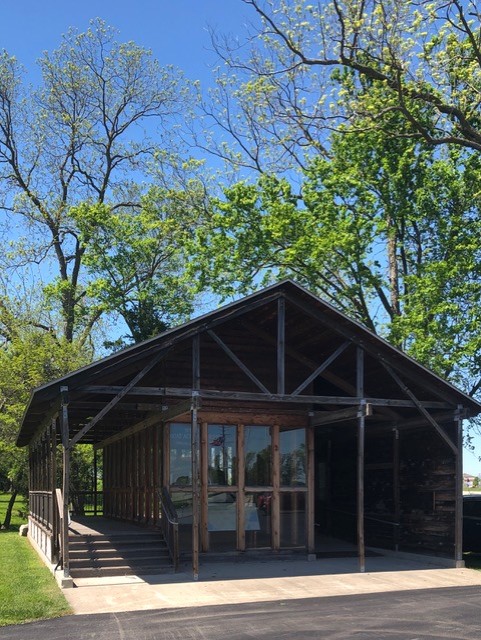
After learning about Santos, I started to look at the Wichita State campus differently. I imagined him frequenting Ablah Library, which holds a collection of his personal writings and was my favorite place to study and write. Although there is no sign or sculpture at Wichita State that visibly marks Santos’ time there, I felt that I was following in his footsteps whenever I walked along the path between the library and the English department offices. I also imagined how lonely it must have been for him while he was living so far from both his home country and the well-established Filipino American communities on the coasts.
Themes of geographic distance as well as the distance created by passing time permeate Santos’ stories set in the Midwest. In the 1955 story “The Day the Dancers Came,” Fil, an older Filipino man, eagerly awaits the arrival of a Philippine dancing troupe, planning to invite them to dinner and give them a tour of Chicago, where they are performing. Fil sees the young Filipinos as a way to reconnect with and relive the happy memories he has of his home country. However, his hopes are crushed when the dancers avoid and ignore his invitations.
Before the dancers’ performance, Fil gets the idea to record the audio of the performance—the stomping of feet, the shouting and singing in dialects—with what he calls his “sound mirror,” a portable tape recorder. In this way, he seeks to preserve the past forever, creating a way to immerse himself in his idealized memories through sound.
As a member of an earlier generation of Filipino immigrants, Fil is not only separated from the Philippines he left by a great distance but also by the cultural changes that happen over time. Having not been back to the Philippines since he left as a young man, Fil knows the country only as he remembers it and is reluctant to accept that that place no longer exists. For him, “time was the villain” because it creates a distance that can never be bridged. He knows that what is lost to time is lost forever, and that clinging to a memory can warp how a person perceives the present: “Like time, memory was often a villain, a betrayer.”
Fil records the performance, but in the end, he fails to preserve his sentimental memories of Philippines, its people, and its cultures. By accident, he partially erases the tape and is left with nothing but confused noise:
“Frantically, he tried to rewind and play back the sounds and the music, but there was nothing now but the full creaking of the tape on the spool and meaningless sounds that somehow had not been erased, the thud of dancing feet, a quick clapping of hands, alien voices and words: in this country… everything… all of them… talking eyes… and the scent… a fading away into nothingness, till about the end when there was a screaming, senseless kind of finale detached from the body of a song in the background, drums and sticks and the tolling of a bell.”
Santos seems to suggest that attempting to preserve the past according to subjective beliefs as to what is important is a fruitless struggle. His stories are often concerned with finding a sense of belonging amidst the changes of modernity, and Santos surely experienced these struggles himself while in the Midwest. However, he accepted the changes that life brought and became an American citizen in 1976, while he was living in Wichita. Eventually, he returned to the Philippines — one he may not have recognized but embraced nonetheless.
When I returned to the Wichita State campus to photograph Ablah Library, I was shocked to see all the construction and renovation going on around campus. The place was still recognizable, but I felt a little melancholy that some of my favorite spots might one day disappear or be replaced. Ironically, Ablah Library itself is an example of this kind of development; built in 1962, it was designed by John Hickman, a student of Frank Lloyd Wright, and was modeled after Wright’s “Prairie Style” that reflected the expansive landscapes of the Midwest through a dramatic emphasis on horizontal lines. The original long, low profile and details such as a concrete cantilevered balcony over the entrance were eventually obscured by new additions to the building.
The world is a palimpsest, constantly overwriting itself. Like people, cultures, and countries, places change with time. It’s unavoidable, and it’s often necessary, but that doesn’t make it hurt less when we lose what means so much to us. Even so, while I struggle to accept change, I take comfort in the fact that no one can ever really alter the past and the impression that it has left on me. When I visit the places that hold special meaning for me, I see ghosts, traces that show: this was a person, this was a place, and this really happened.
Abby Bayani-Heitzman was born and raised in northeast Kansas, where she continues to live and work. She received her MA in English from Wichita State University and participated in the second cohort of the Kansas Creative Arts and Industries Commission’s Critical Writing Initiative. Since 2020, she has served as coordinator for the Filipino American community organization Malaya Kansas, a chapter of Malaya Movement USA




![Twain in study window 1903 Mark Twain in Study Window [1903]](https://newterritorymag.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/Twain-in-study-window-1903.jpg)