Malcolm X
3448 Pinkney Street
Omaha, Nebraska
By Ashley M. Howard
My 1980s childhood included reading to my Cabbage Patch Kid in a neon bean bag and practicing my moves so that I could dance with MC Scat Cat. I was (am) a nerd. I loved school. And with exception to the week set aside for standardized testing (shout out to Iowa Test of Basic Skills), field trips reigned as the most exciting occasions.
In Omaha, where I grew up, trips to the railroad museum and zoo were standard. Once when we visited the Mormon Pioneer Cemetery, I tripped and fell face first into a spiked wrought-iron fence. Relatively unscathed, I returned to the school cafeteria where my third-grade classmates and I shook a mason jar filled with cold cream until our little arms turned to mush.
It was a good day. We ate fresh baked bread and homemade butter. I didn’t lose an eye.
Another time our plaid-clad mob loaded onto a yellow bus bound for Hastings. At the end of the two-hour drive, we met global legend, well at least People magazine feature fowl and Tonight Show guest, Andy the Footless Goose.
These trips reinforced the mythologized stories taught to me about Nebraska history. Wide-open prairies, bustling stockyards, brave pioneers, and wholesome Heartland values. Absent were the stories of the displaced Pawnee, Ponca, Omaha, and Oto-Missouria Peoples. Erased were the Black, Asian, and Latinx workers who butchered livestock and built railroads. The state’s ugliest moments, those that challenged claims of Midwestern meritocracy, were swept under the rug.
Both within the popular imagination and much of the scholarly discourse, the Midwest is normalized as an exclusively white place—frozen in the past, albeit one dissociated from actual historical reality. Politicians, journalists, and everyday citizens regard the region with deep nostalgia; a “museum-piece” of a bygone era in times of great uncertainty.
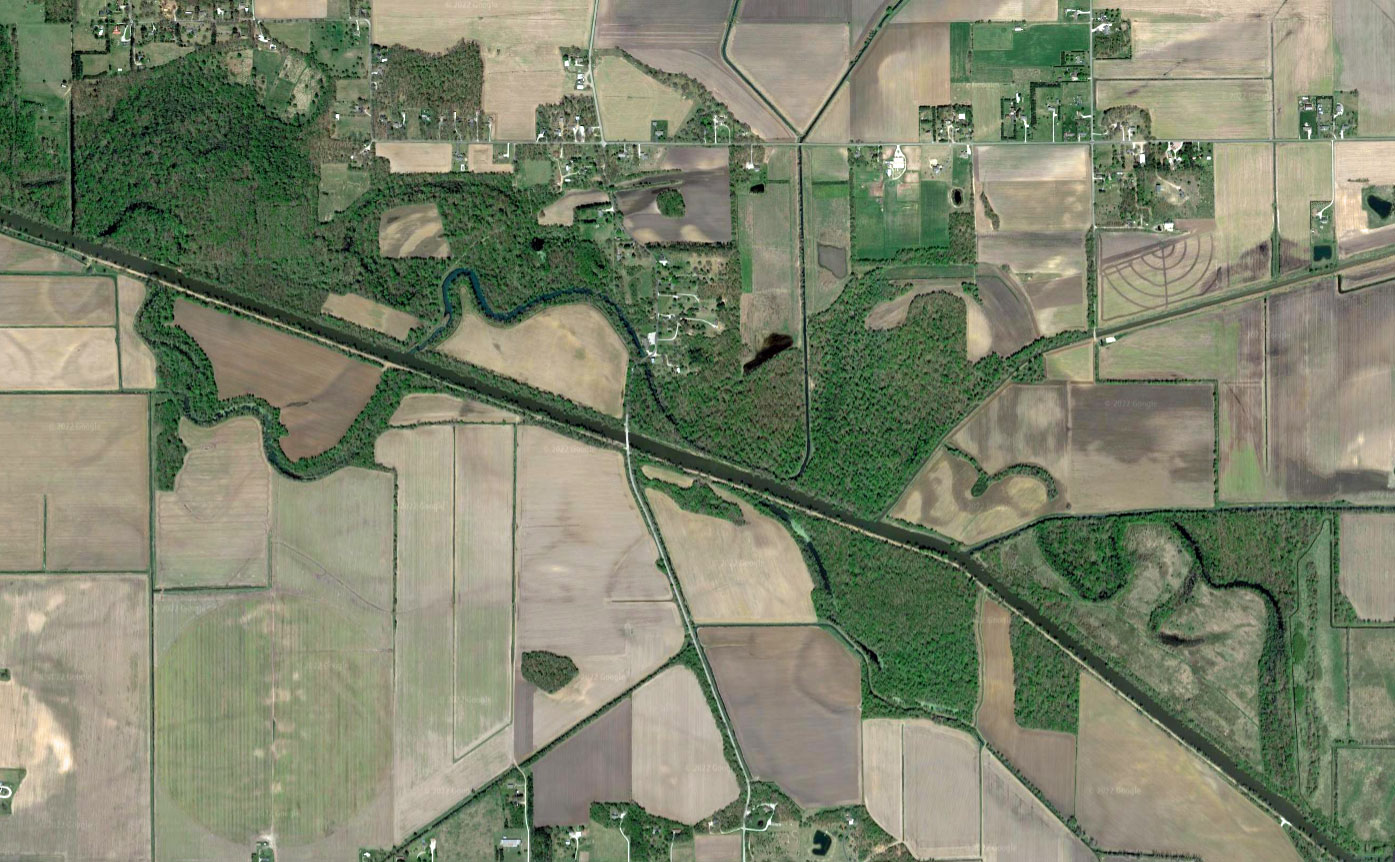
I was in my thirties and a professor of African American history when I finally took my own field trip to the birth site of Malcolm X, Omaha’s oft-forgotten native son.
The opening pages of Malcolm X’s autobiography, and arguably his political radicalization, begin in Omaha. In the chapter “Nightmare,” Malcolm shares a vivid description, recounted to him by his mother, Louise Little. One evening the Ku Klux Klan rode on their home to intimidate the family into fleeing. Heavily pregnant with her fourth child, while her husband was travelling, Mrs. Little stood her ground as the terrorists “galloped around the house, shattering every windowpane with their gun butts. Then they rode off into the night, their torches flaring, as suddenly as they had come.” The Littles welcomed their son, Malcolm a few months later and remained for two more years. Although Omaha is not mentioned again in the five-hundred-page book, the violence his family experienced throughout the region looms large.
In death, as in life, Malcolm X is a divisive figure. An admitted hustler, convicted felon, racial separatist, Muslim, and provocative orator, his brilliance resonated deeply with millions across the African diaspora. Yet the memorialization of his first home at 3448 Pinkney proceeded at a near glacial pace, due in part to his political views and skepticism that one of the nation’s most prominent Black leaders hailed from Nebraska. This delay is especially stark when compared to Atlanta’s 38-acre Martin Luther King, Jr. National Historical Park, consisting of dozens of buildings managed by the National Parks Service.
If we consider that physical sites promote our most sacred historical myths, this really should come as no surprise. America now embraces King and the sanitized narrative of his activism as proof of this nation’s redemptive, triumphalist narrative arc. Narrators distill racism as contained to the south and eradicated through the efforts of activists and federal legislation. The blocks-long King site affirms this illusion.
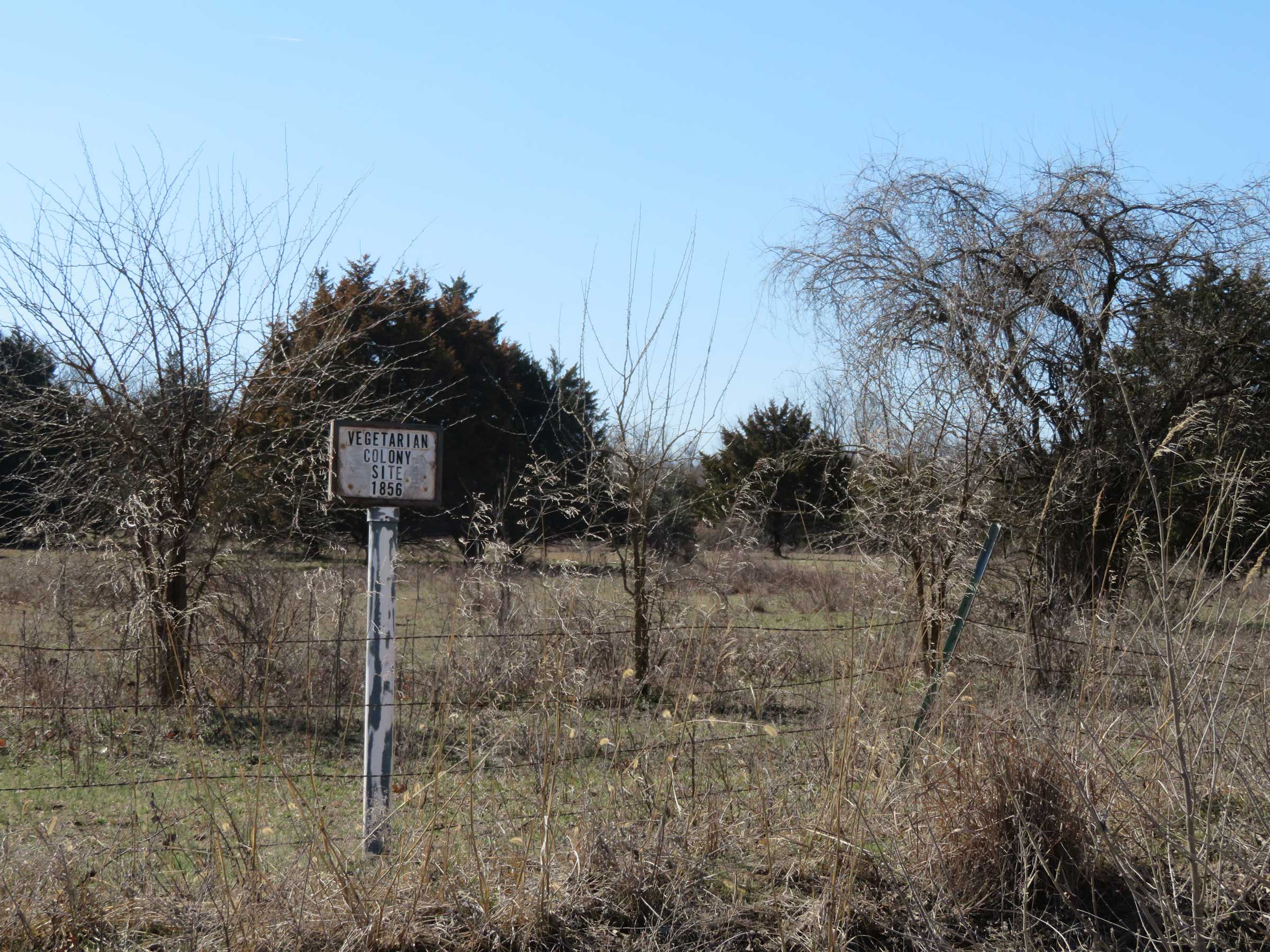
The Littles’ Omaha experience and the on-going struggle to create an adequate memorial of their son challenges this framework and breaks open the comfortable history of the Midwest. The Klan threatened the young family on account of Earl and Louise Little successfully organizing with the Omaha branch of the Universal Negro Improvement Association. Founded by Marcus Garvey in 1914, the pan-Africanist organization promoted Black economic independence and racial pride, representing a freedom agenda distinct from the integrationist model.
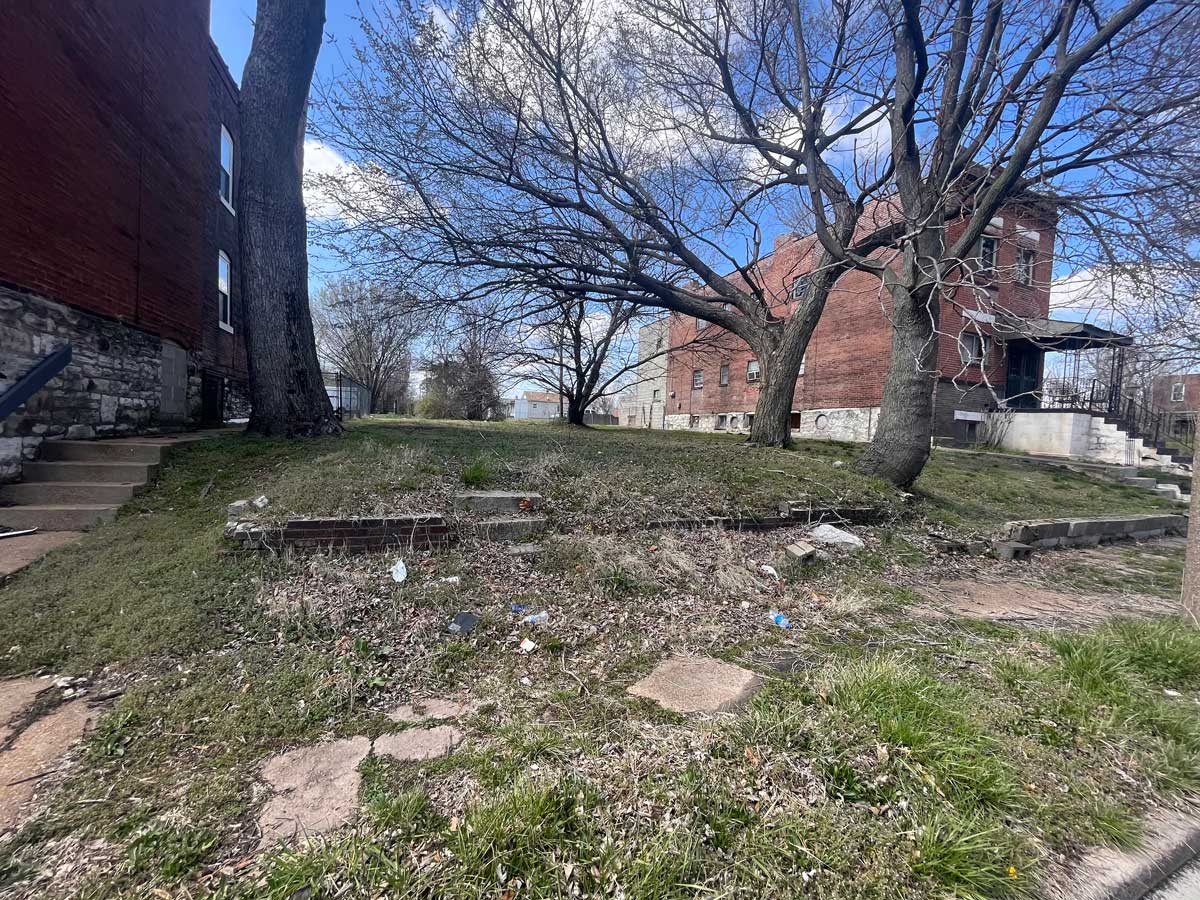
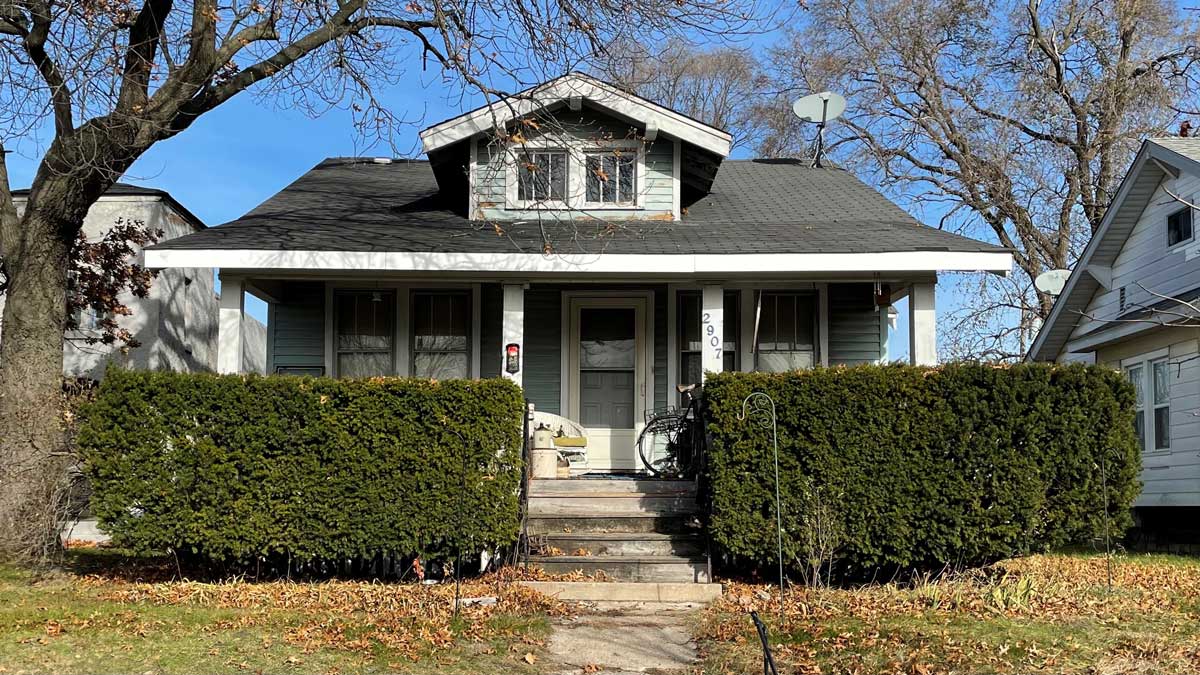
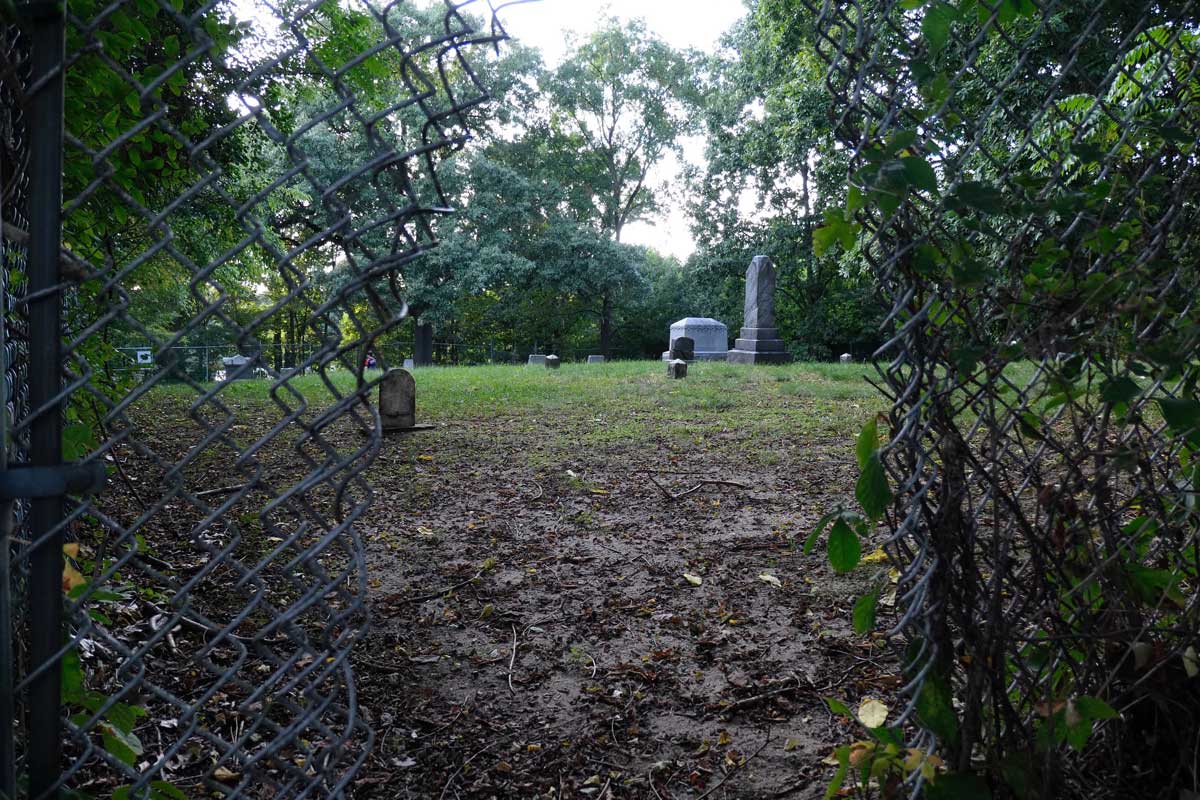
The struggle for recognition of Malcolm X’s home is a continuation of this tension. The city razed the modest house on Pinkney in 1965, the year Malcom was assassinated. That building’s destruction was the result of ignorance, not malice. But the wholesale demolition of homes on the surrounding blocks is indicative of the inherent racism of urban renewal.
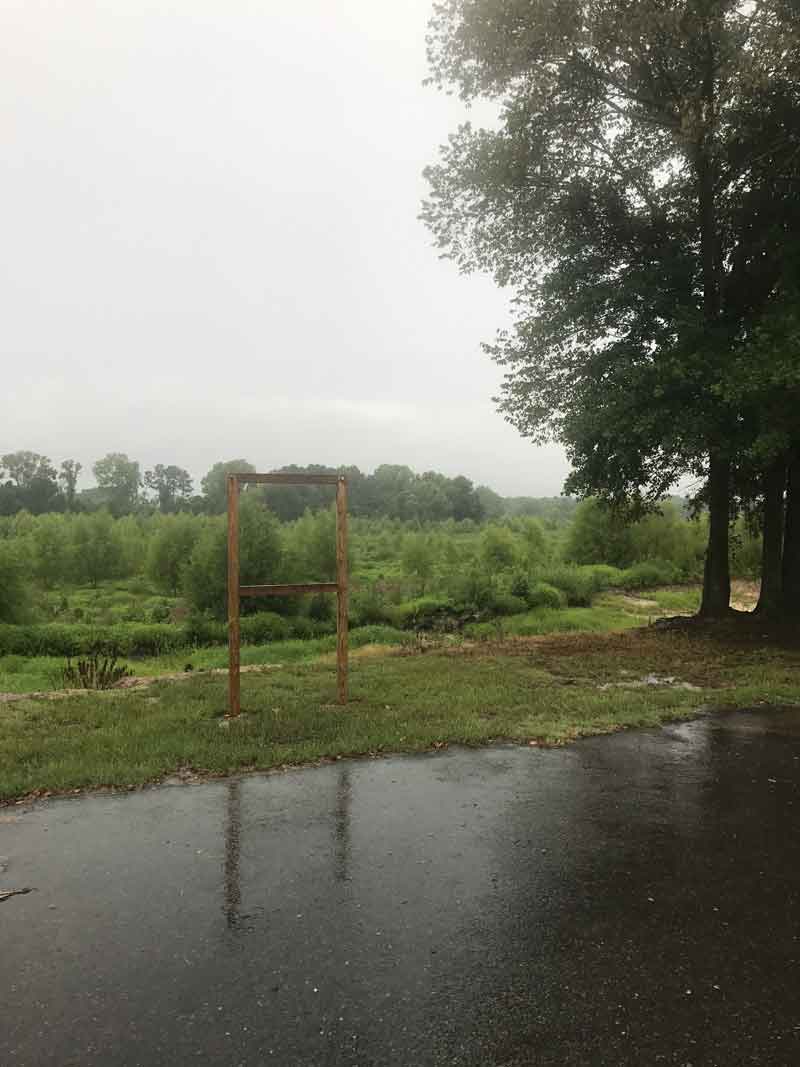
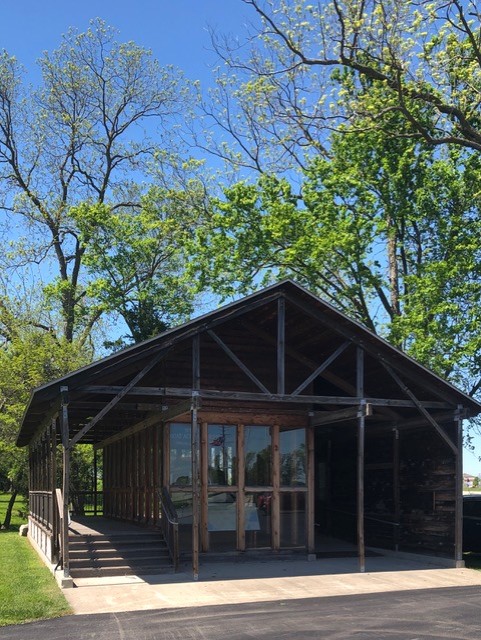
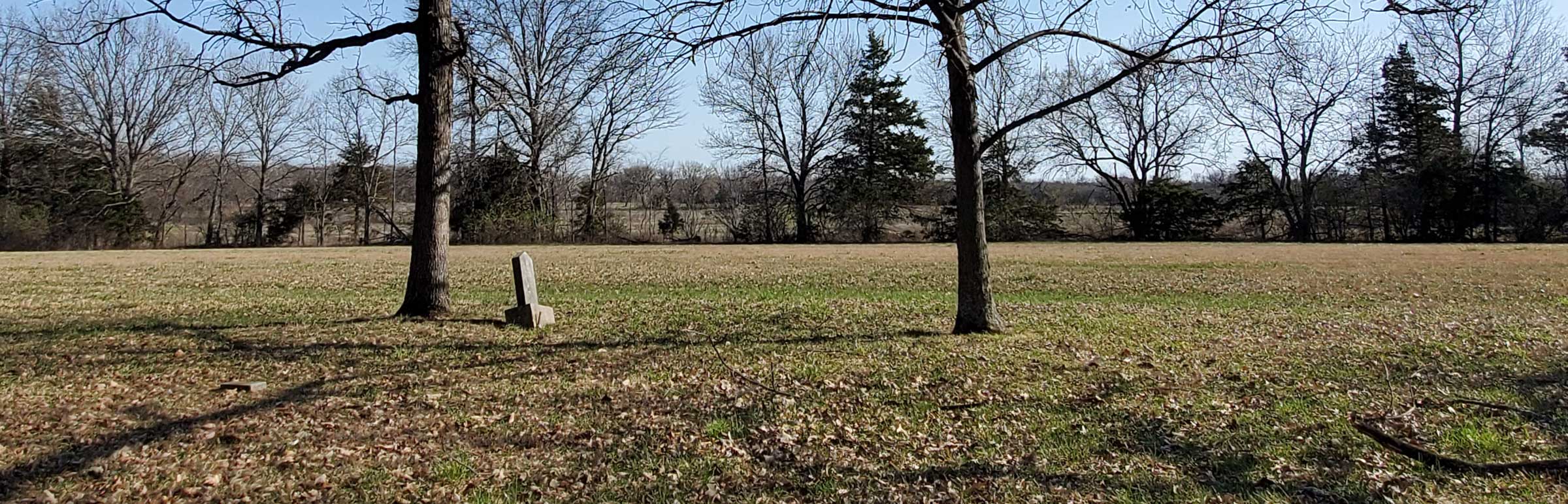
In 1970, activist and former resident of the home Rowena Moore began the Malcolm X Memorial Foundation. While the Nebraska Historical Marker Program quickly approved the sign, another two decades passed until it was placed. On May 19, 1987, on what should have been Malcolm X’s sixty-second birthday, the official state marker was dedicated. When I visited over a decade ago the marker stood, a lone sentinel in an overgrown lot, isolated from Malcolm X’s activism and the vibrant community.
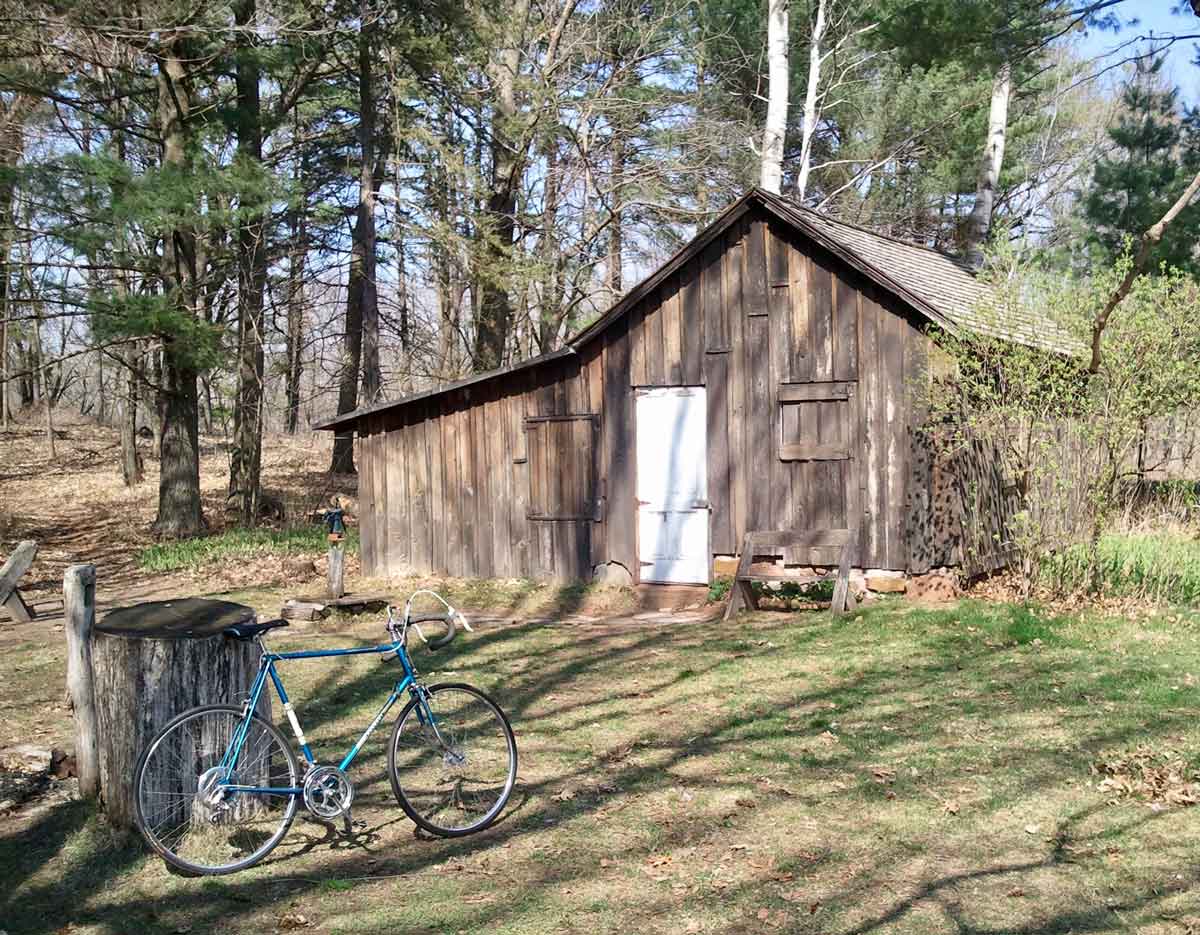
Today, that spirit is renewed. In 2018, artist and land activist Jordan Weber constructed the 4MX greenhouse, conceived as a place to nurture seedlings and people. When standing in the greenhouse with its double doors open wide, the marker is perfectly framed between them. Its final four words read “His teaching lives on.”
What might schoolchildren learn from a visit to this site? By reinscribing Malcolm X on to the landscape, his legacy comes to the fore. Put simply, this means a radical retelling of Omaha’s history. That retelling includes stories about Moore’s work organizing women meatpackers as well as Black high school students staging a walkout on May 19, 1969, demanding racially affirming educational experiences.
These histories also generate new questions: What were the work and educational experiences of Black Omahans? Why are there no local streets, government buildings, or schools bearing Malcolm’s name? Why were 311 historical markers erected around the state before one honored the contributions of a Black Nebraskan?
Neighborhood divestment and stigmatization ensures that no one will happen upon Malcolm X’s birthplace. One must intentionally seek it out. And like the physical marker, Omahans must also journey to seek answers to the above questions.
Through a deep engagement with Malcolm X’s Omaha experience, students will locate the rich social, intellectual, cultural, and political life of the city’s Black residents. In (re)visiting these sites, a more complex portrait of the construction and maintenance of Midwestern mythologies emerges. Such field trips to the past provide a roadmap to a more inclusive history and future. To supplement the white bread snack (and history) of my youth with colorful, community grown veggies is delicious indeed.
Ashley Howard is an assistant professor of History and African American Studies at the University of Iowa. A proud Omahan, her research interests include violence, social movements, and the Black Midwest.
Photo by Chris Machian.