Toni Morrison
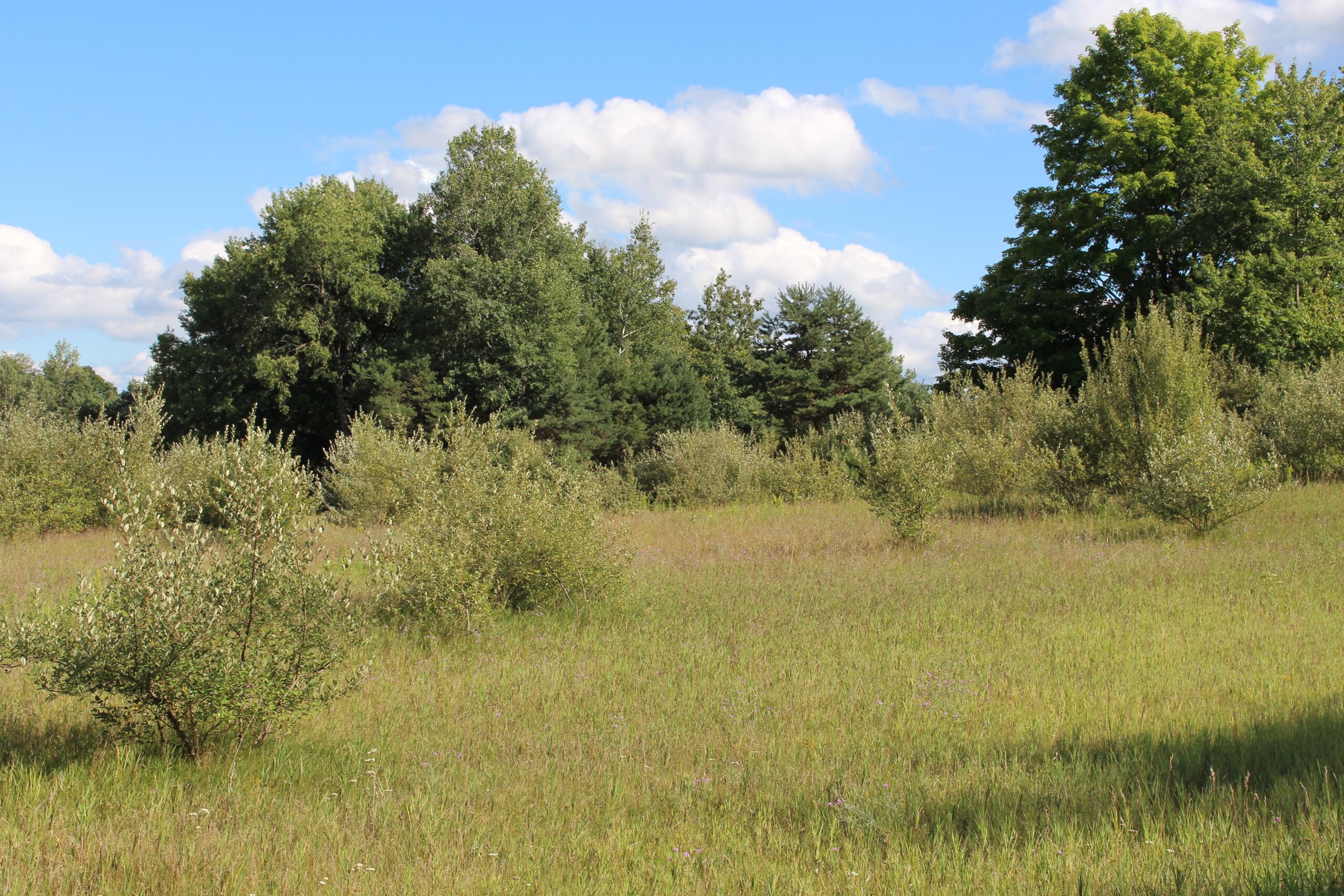
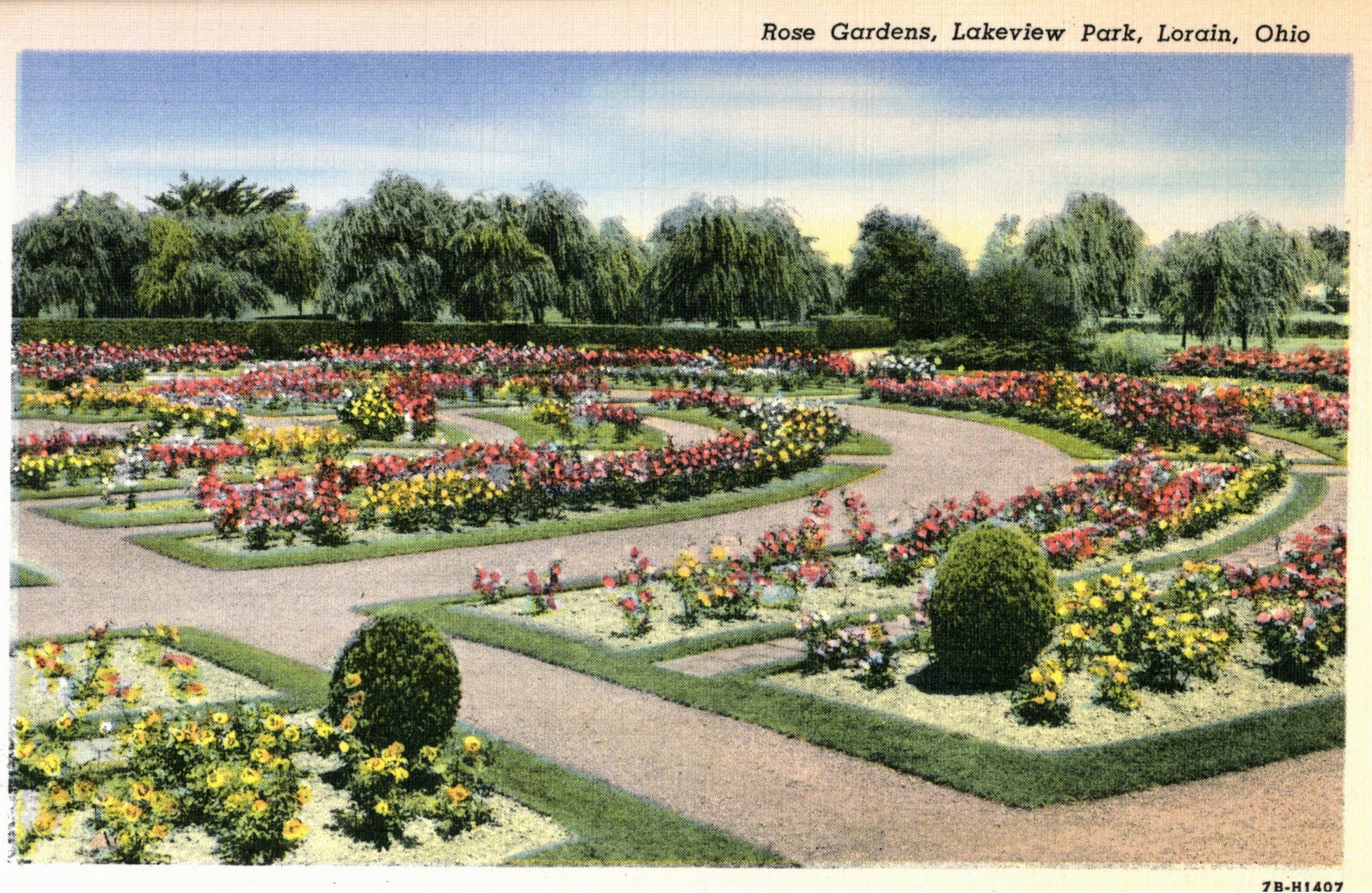
Lakeview Park
Lorain, Ohio
By Ashley Burge
As a teenager, I entered what Toni Morrison calls her narrative “village” through her first book, The Bluest Eye (1970), and I was pleased to see three young Black girls traverse the familiar experiences of home life while prodding the unfamiliar territory of adolescence. I found much comfort in these girls’ fantasies and fears, and I wept, as I still do, over their tragedies. I was also entranced by the way Morrison framed her beautifully tragic characters in picturesque settings of nature and growth and beauty. Any serious Morrison reader is well attuned to her complex and intriguing characters, sparse but rich prose, and “unspeakable” thematic materials. I remember sprawling on my bed admiring these Black girls amidst golden-brown autumn leaves or tight red rosebuds. To me, these snapshots of nature were a buffer to the hopelessly tragic story that would soon unfold.
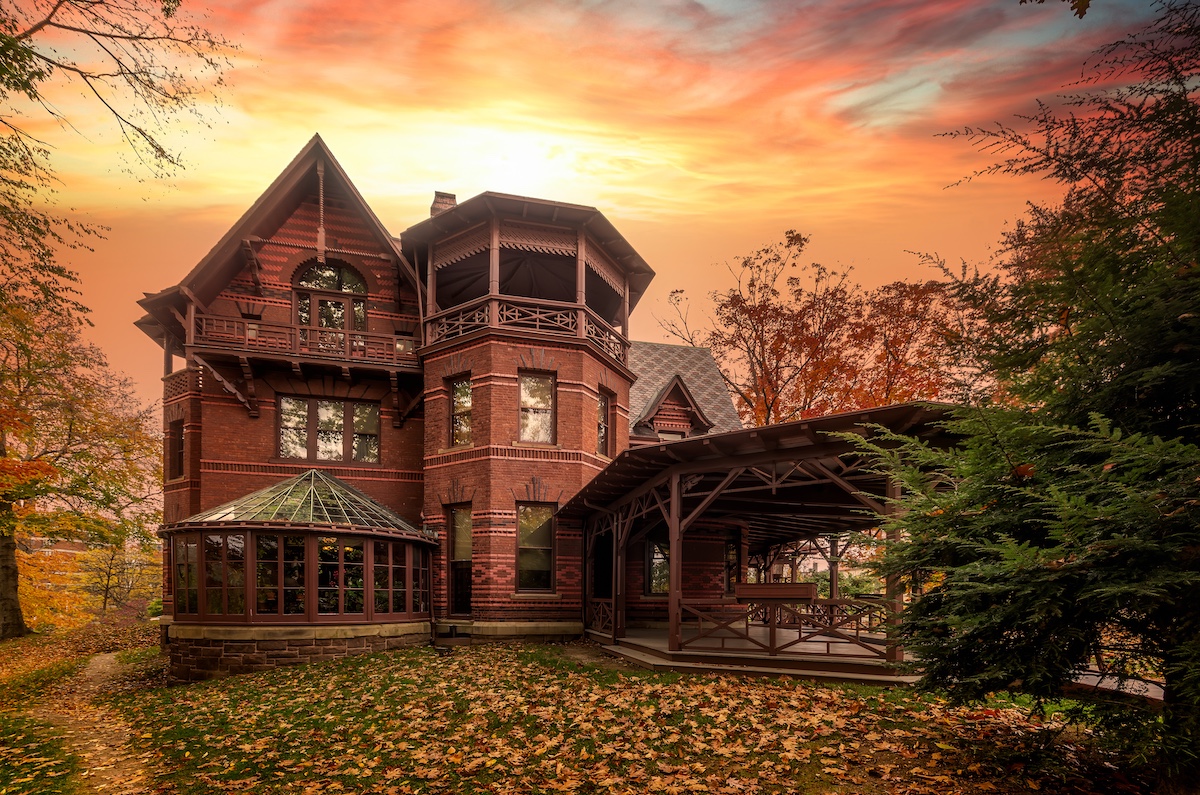
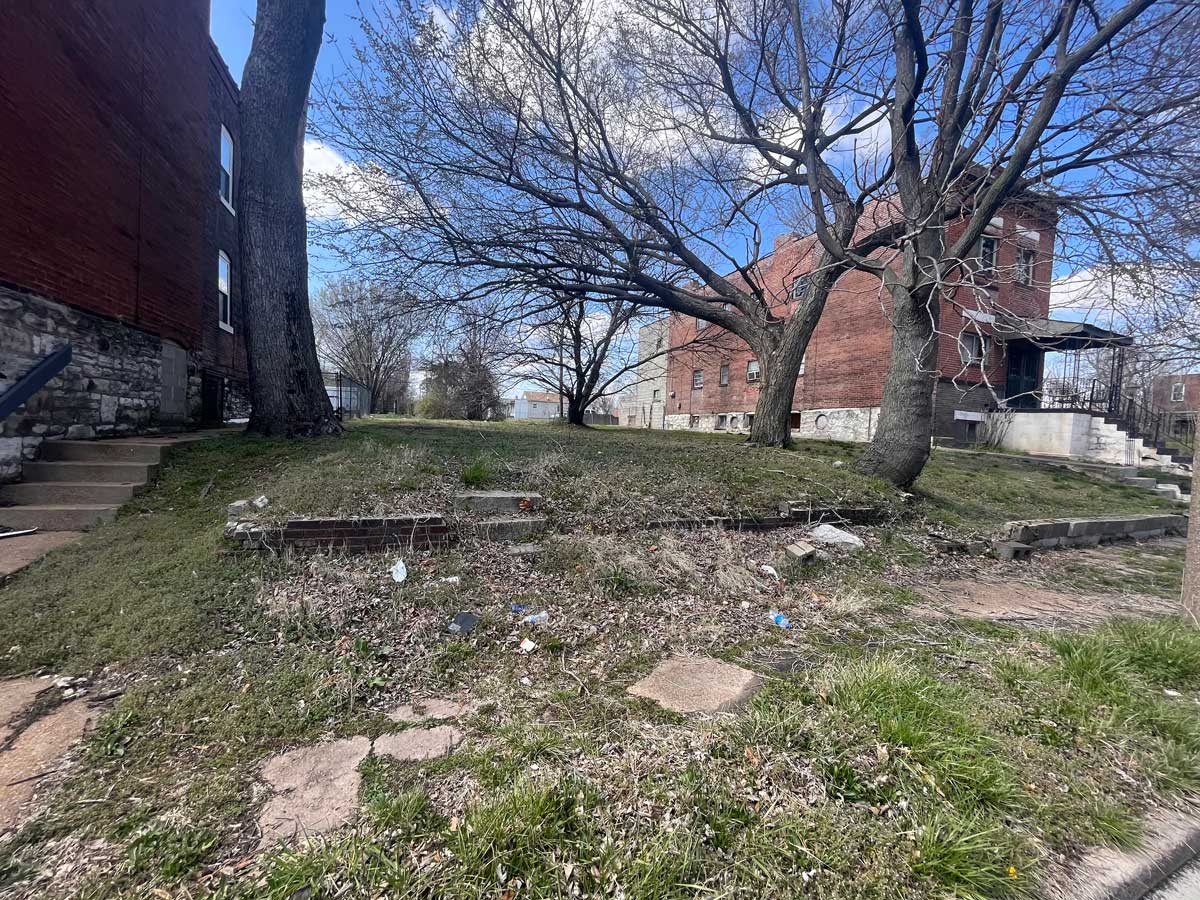
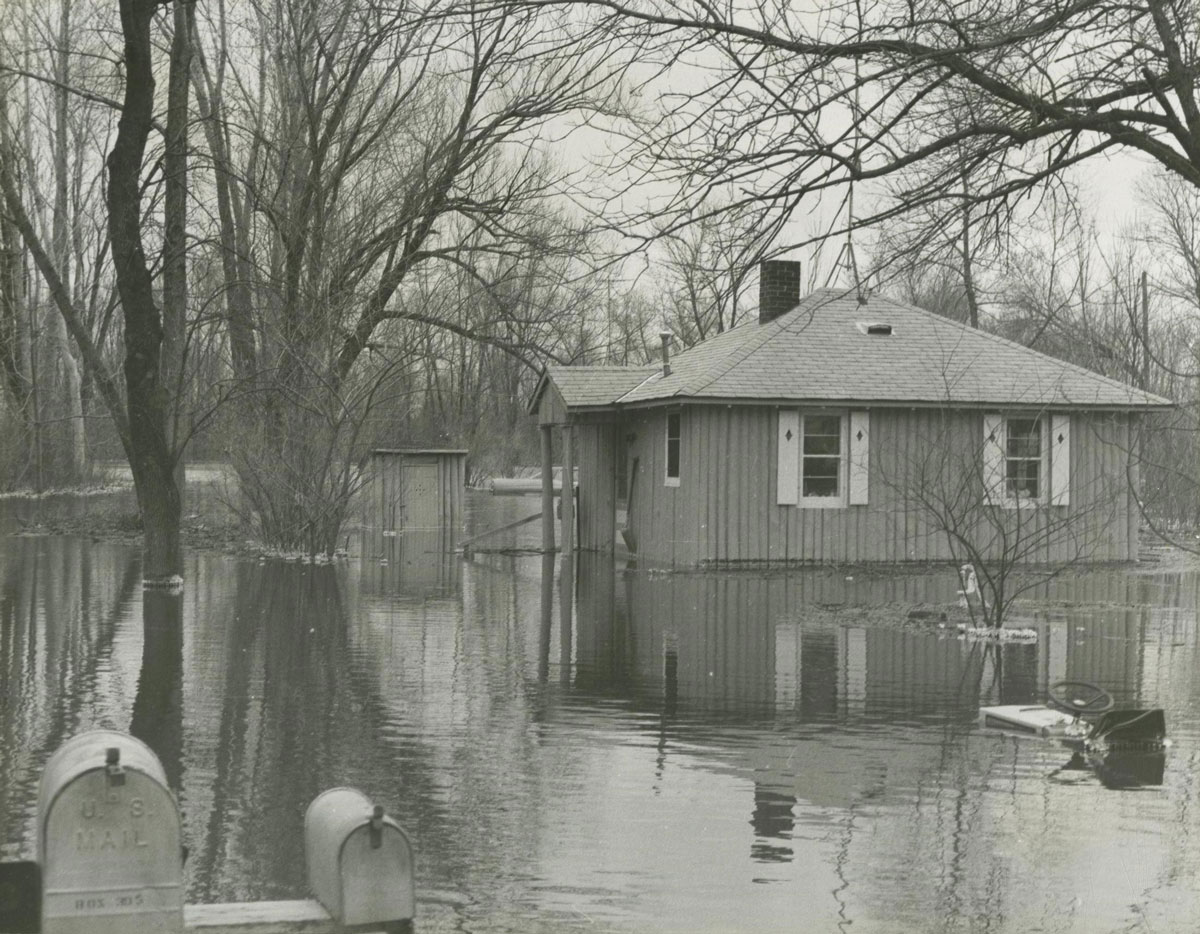
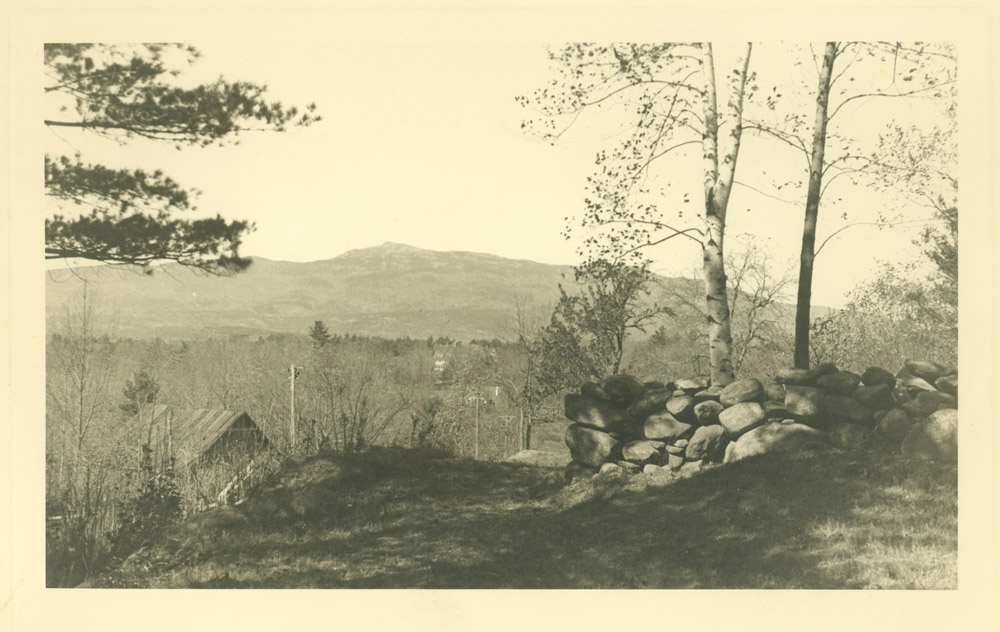
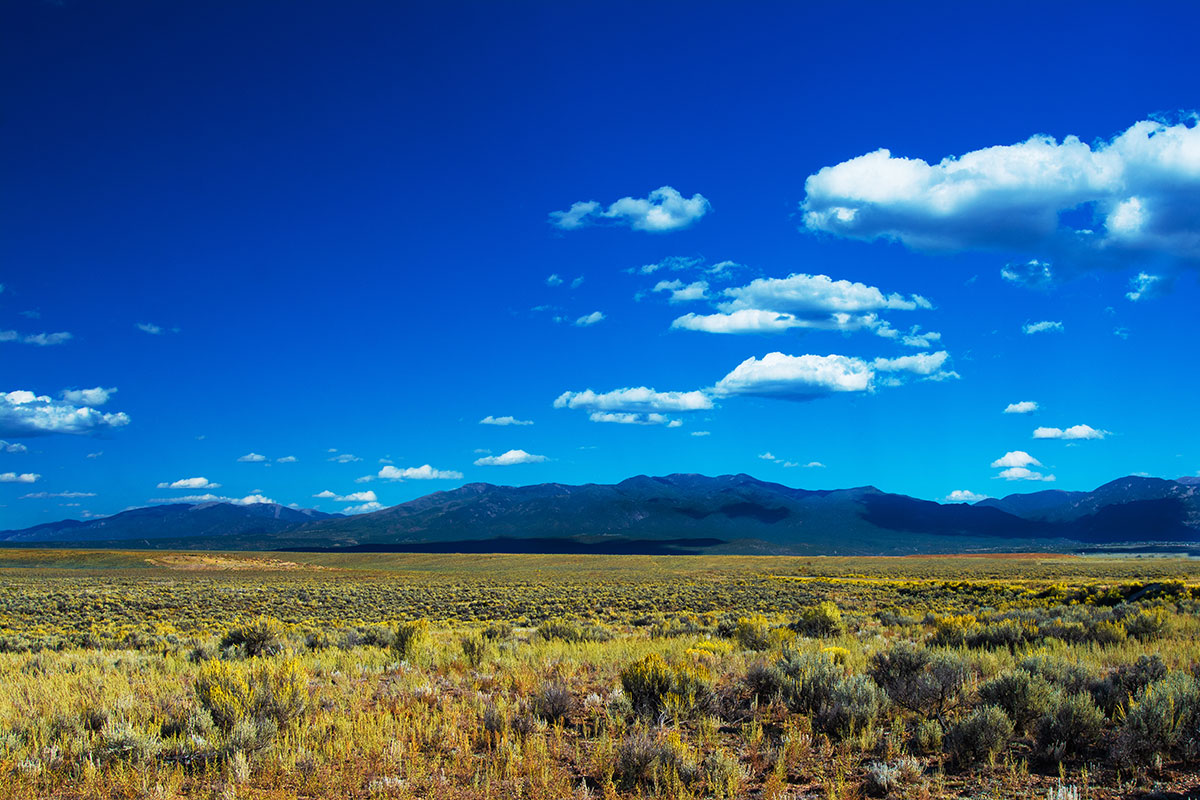
In The Bluest Eye, Morrison uses the backdrop of Lorain, Ohio, her midwestern hometown, to illuminate the traumas inflicted on young Black girls and women in the 1940s. Specifically, she represents the Edenic Lakeview Park, with its beautiful rose gardens, situated among the pristine beachfronts on West Erie Avenue, as a pathway to cathartic revelation and renewal. For Morrison, nature and the natural world are a catalyst for survival, so the book’s version of Lakeview, called Lake Shore Park, is an ideal space to anchor her vision.
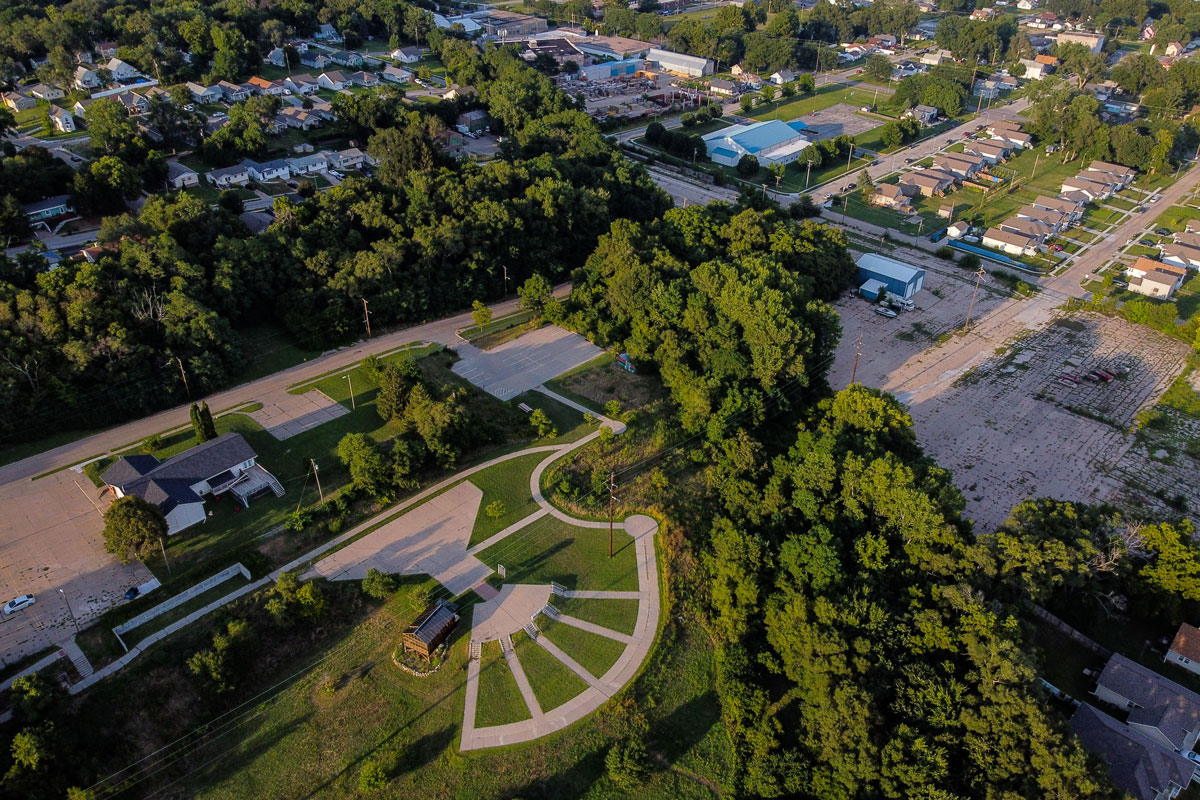
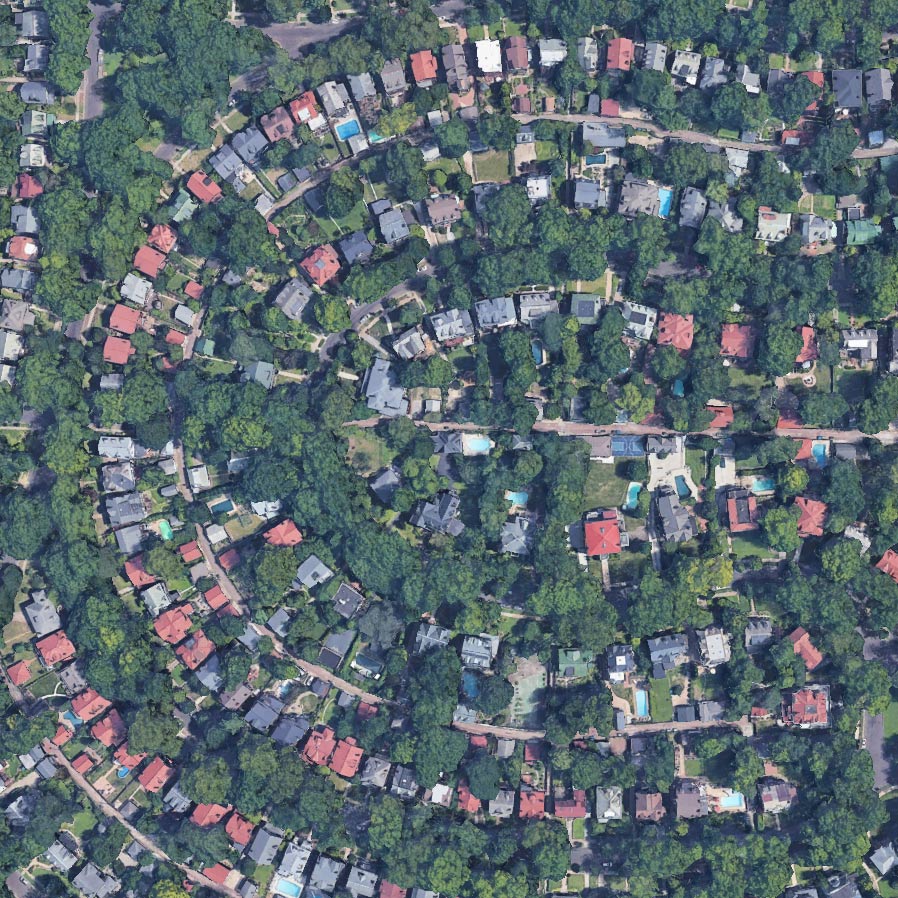
Lakeview Park has become a landmark in Lorain County with its approximately 2,500 roses planted in a rotary wheel. The park sits on Lake Erie, its circular design symbolizing wholeness and rebirth. In a more just world, it would be the ideal space for Morrison’s tragic protagonists to transcend the confines of intersectional oppression. But in 1940s Lorain, Ohio, spaces such as these were inaccessible to the three Black girls who epitomize themes of victimhood and survival in Middle America. In The Bluest Eye, these girls, Claudia, Fredia, and Pecola, are accosted by the traumas of racism, sexism, and classism well before they have escaped the naïve joy and confusion of adolescence. The tragic character Pecola does not understand or question her obsessive desire for blue eyes, but she is awestruck when the green-eyed “high-yellow dream child” Maureen Peal enchants teachers, parents, and students. Portrayed as a type of Persephone embodied in Morrison’s season themed narrative, Maureen disrupts the equilibrium of the girls’ identities and symbolizes the overwhelming otherness of Black girlhood in America. In these young girls’ experiences with racism and sexism, Morrison interrogates the worst possible scenarios for those who are othered, marginalized, and dismissed, and she indicts the communities that are complicit in their annihilation.
In many ways, The Bluest Eye is an autobiographical rendering of Morrison’s own othered identity in the small Midwestern industrial town of Lorain, Ohio. Morrison adamantly affirmed her Midwestern roots throughout her career. In conversation with Collette Dowling, she said, “Everything I write starts there…. Whether I end up there is another question, but that’s the place where I start…. It’s my beginning, my ‘thing,’ and I have distorted it, piled things on, I have done whatever it is that writers do to places, and made it my own. So it is mine now.” Even while claiming the Midwest as her own, she confessed to Robert Stepto, “I know that I never felt like an American or an Ohian or even a Lorainite.”
Morrison’s allegiance to the Midwest shows in her ability to carve out the validity of Black identity in a region that often silences diverse voices. Morrison’s family faced such disenfranchisement. Before relocating to the Midwest for better opportunities, they had deep roots in the South, with her mother being from Alabama and her father from Georgia. She often recounts the story of 88 acres of land that were legally taken from her Native American maternal great-grandmother to show how white supremacy and systematic oppression renders land inaccessible to Black and brown people.
Morrison emphasizes this extension of day-to-day oppression in The Bluest Eye as she traces the growth and then disintegration of Pecola’s character. Before a pivotal scene in which Pecola is rejected by her mother and humiliated in front of the little white girl who her mother cares for, Morrison details the natural beauty of the white neighborhood that these young girls cannot access:
“We reached Lake Shore Park, a city park laid out with rosebuds, fountains, bowling greens, picnic tables. It was empty now, but sweetly expectant of clean, white, well-behaved children and parents who would play there above the lake in summer before half-running, half stumbling down the slope to the welcoming water. Black people were not allowed in the park, and so it filled our dreams.”
Here, Morrison embosses the fictionalized Lake Shore Park onto Lorain’s own Lakeview Park, with its lush rose gardens, manicured lawns, and picturesque lakeside. The tragedy of its beauty is that these young Black girls in 1940s Lorain are denied access to the dream of smelling those rosebuds, playing on those lawns, or frolicking on that lakeside. They are shut out from its beauty in nature and, therefore, alienated from their community, which adds to the despair that leads to Pecola’s demise.
When I reflect on my first immersion into The Bluest Eye as a teenager, I realize that my delight in Morrison’s poetic rendering of nature points to the reclamation of spaces that have been historically inaccessible to the Black community. Within that legalized denial enacted prior to the 1960s there was not only the unspoken denial of the ecstasy of nature but also the disenfranchisement of property, wealth, and mobility that still plagues Black Americans today. I was not personally denied access to Lorain’s natural enclaves, but the tragic narrative of denial was a tangible specter that haunted my hometown of Birmingham, Alabama even in my adolescence.
These are, perhaps, the sentiments that impressed upon me as I empathized with Claudia, Frieda, and Pecola. And these are, perhaps, the sentiments that many Black Americans must navigate as they encounter the traumas connected to public parks and natural resources in America. It would not be difficult to surmise that Morrison incorporates the tragic denial of Lake Shore Park in her narrative because her desire to access its beauty and nature also dominated her own dreams as a child. However, Morrison’s novels never persist in the tragic nor linger too long into despair. At their core, they are about healing that can lead to survival and subjectivity. In The Bluest Eye, Morrison took the pang of rejection and adorned the park with flourish and meaning and gravitas and three little Black girls whose voices would have otherwise been silenced. Now, Lakeview Park is forever hers, and through her reclamation, it becomes ours.
Dr. Ashley Burge is an Assistant Professor of African American literature at Augustana College–Illinois specializing in 19th and 20th century African American literature. Her research and teaching emphasize the intersections of race, gender, sexuality, and class. She also explores Black feminism and ecocriticism in her writings. Her essays have appeared in the North Carolina Literary Review, the Pennsylvania Communication Annual, the African American Encyclopedia of Culture, and the critical anthology Through Mama’s Eyes. Her current book project establishes a theoretical paradigm that transmutes trauma and fragmentation to wholeness and subjectivity in African American literature.




![Twain in study window 1903 Mark Twain in Study Window [1903]](https://newterritorymag.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/Twain-in-study-window-1903.jpg)